The New Social Contract: Microsoft Taps LinkedIn’s Data Trove for AI Supremacy
Starting November 3rd, the professional lives of a billion users become the training ground for Microsoft’s AI ambitions, raising profound questions about data, consent, and the future of work.
In a move that reverberates across the digital professional landscape, Microsoft is set to begin using data from its subsidiary LinkedIn to train its artificial intelligence models, a policy taking effect on November 3, 2025. The professional networking giant, with over a billion members worldwide, will by default opt-in users in several regions—including the UK, EU, Canada, and Hong Kong—to have their public profiles, posts, skills, and job application data fed into Microsoft’s sprawling AI ecosystem.
This decision marks a pivotal moment in the age of generative AI, transforming the meticulously curated career histories of millions into a valuable resource for technological advancement, while igniting a firestorm of privacy concerns and regulatory scrutiny.
The policy change allows Microsoft to leverage LinkedIn’s vast and unique dataset—a detailed chronicle of the global workforce’s skills, experiences, and connections—to enhance its AI-powered features across a suite of products. This includes improving everything from job recommendations and content personalization on LinkedIn itself to powering more sophisticated models within Microsoft’s broader ecosystem, such as its Azure OpenAI service. The explicit goal is to create more intelligent tools that can better connect professionals to opportunities, a vision already taking shape through new AI-driven features designed to help job seekers find better matches and recruiters source talent more efficiently.
“AI is democratizing expertise across the workforce. Our latest research highlights the opportunity for every organization to apply this technology to drive better decision-making, collaboration — and ultimately business outcomes.” - Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, Microsoft.
The transition, however, has not been without controversy. The default opt-in nature of the data usage has drawn sharp criticism from privacy advocates and government bodies, including the Dutch privacy watchdog, which warned that once personal data is absorbed into a training model, it becomes nearly impossible to remove. This raises significant questions about user consent and data permanence in an era where personal information is the fuel for AI innovation. LinkedIn has emphasized that private messages will not be used and that users can opt-out through their privacy settings, but the onus is placed squarely on the individual to navigate these controls before the deadline.
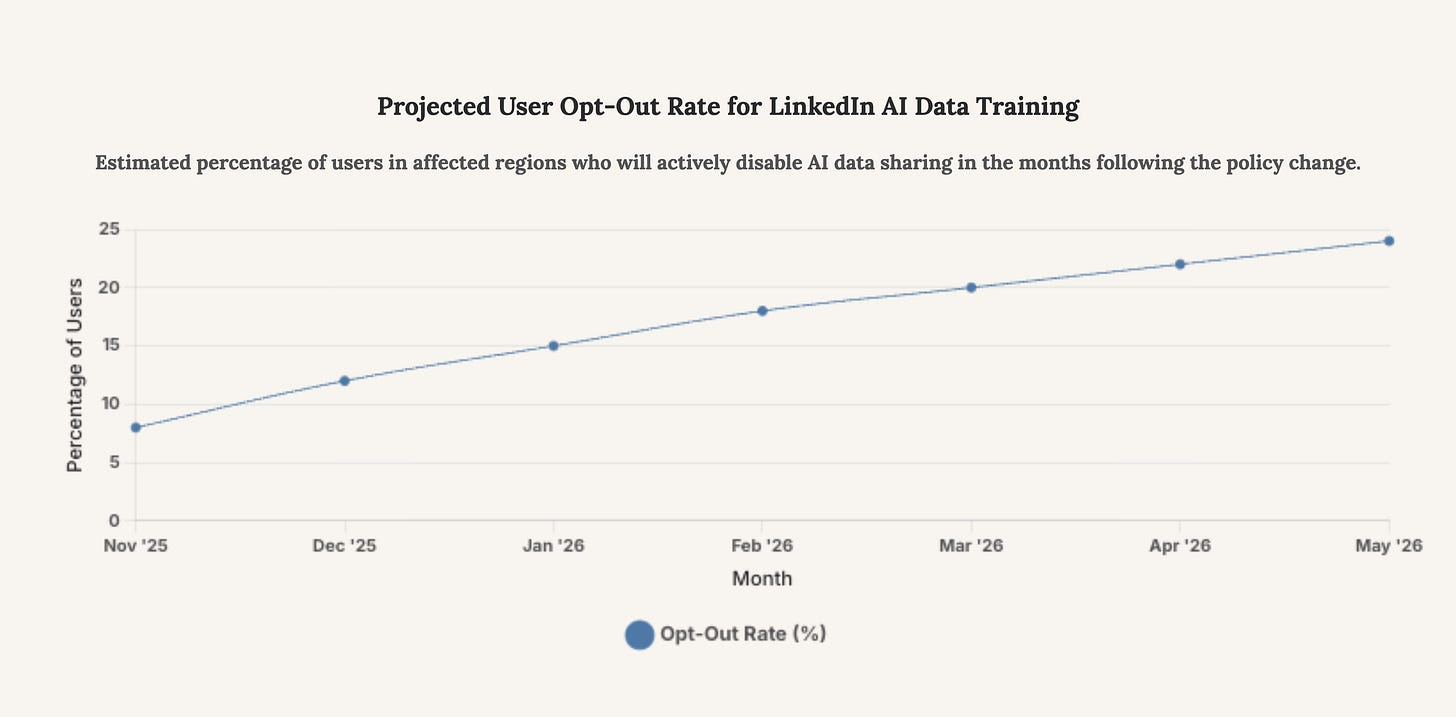
This chart projects the potential rate at which users in the newly affected regions might choose to opt-out of having their data used for AI training. The initial spike reflects the immediate reaction to the policy change, followed by a more gradual increase as awareness spreads through media coverage and word-of-mouth.
Microsoft and LinkedIn’s strategy is emblematic of a broader industry trend where the vast repositories of user-generated content are being repurposed to train the next generation of AI. The ultimate aim is to create a more personalized and efficient digital experience. For job seekers, this translates into AI tools that can interpret conversational queries to find roles that align with their skills and aspirations, even if they don’t match exact keywords. For recruiters, it means AI-assisted sourcing that can identify qualified candidates with greater speed and precision, and even help draft outreach messages.
“Before I send an email to Satya, I use Copilot to make sure I sound Satya-smart.” - Ryan Roslansky, CEO, LinkedIn.
This quote from LinkedIn’s CEO highlights the growing reliance on AI, even at the highest executive levels, to refine communication and strategy. It underscores the deep integration of these tools into daily professional workflows.
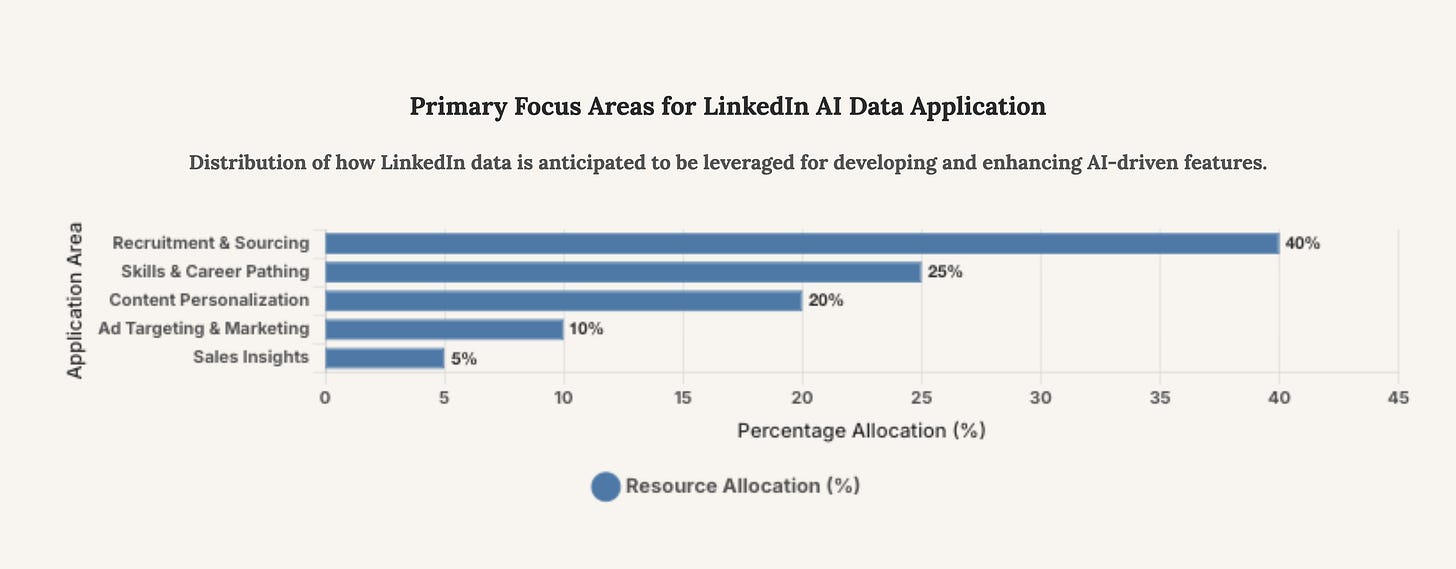
The allocation of LinkedIn’s data for AI development is expected to heavily favor recruitment and talent-sourcing tools, reflecting the platform’s core business. Significant resources will also be dedicated to enhancing skills analysis for career guidance and personalizing the content feed to increase user engagement.
As Microsoft forges ahead with its AI ambitions, the company is navigating a complex landscape of innovation, user expectation, and regulatory oversight. The 2024 Work Trend Index, a joint report from Microsoft and LinkedIn, revealed that 75% of knowledge workers are already using AI at work, often bringing their own tools to the office. This grassroots adoption signals a workforce eager to embrace AI’s potential. Yet, it also puts pressure on companies to provide a clear vision and framework for its use. The decision to utilize LinkedIn’s data is a clear move by Microsoft to build that framework and solidify its position as a leader in the AI revolution.
Ultimately, the integration of LinkedIn data into Microsoft’s AI training pipeline represents a fundamental shift in the value proposition of professional networking. What was once a static digital resume and networking tool is now a dynamic, living dataset powering intelligent systems. The professional identities we cultivate online are no longer just for human eyes; they are actively shaping the artificial intelligence that will, in turn, reshape our careers. This new reality presents both immense opportunity and a critical need for transparency and user control, a balance that will define the next chapter of our digital working lives.