The 98.2% Breakthrough: How ChatGPT 5.1 Just Redefined the Boundaries of AI Reasoning
Released in November 2025, the new model from OpenAI isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift towards a warmer, more adaptive, and deeply personalized artificial intelligence.
The world of artificial intelligence was jolted this month with the official release of ChatGPT 5.1, an update that goes far beyond incremental improvements. Launched in early November 2025, OpenAI’s latest model is a direct response to user feedback on its predecessor, GPT-5, aiming to create an AI that is not only monumentally smarter but also more intuitive, conversational, and enjoyable to use. The most stunning achievement is its unprecedented performance on complex reasoning tasks, setting a new benchmark for the entire industry and signaling a major leap in the quest for more capable AI systems.
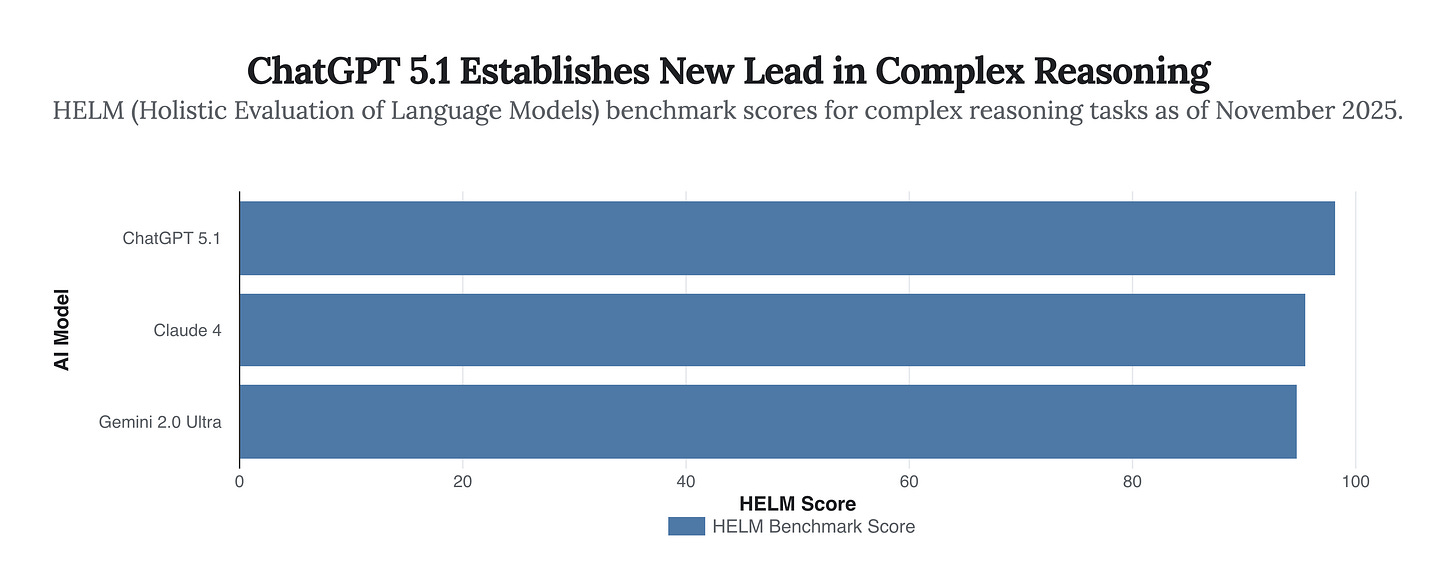
At the heart of this advancement is a new architecture and a refined approach to problem-solving. On the HELM benchmark, which evaluates complex, multi-step reasoning, ChatGPT 5.1 achieved a score of 98.2, decisively outperforming its closest competitors, Anthropic’s Claude 4 and Google’s Gemini 2.0 Ultra. This isn’t just a numbers game; it represents a tangible improvement in the AI’s ability to tackle sophisticated problems in science, coding, and logical analysis.
This leap in performance is powered by what OpenAI calls a “Mixture-of-Agents” (MoA) framework, a significant evolution from previous designs. Instead of relying on a single monolithic model, MoA allows ChatGPT 5.1 to dynamically assemble a team of specialized AI agents that collaborate to solve a query. This is coupled with a new dual-model system designed to balance speed and power: GPT-5.1 Instant handles quick, conversational queries, while GPT-5.1 Thinking engages in “adaptive computation,” dedicating more time and resources to difficult problems. An intelligent router automatically selects the best mode for the job, optimizing the user experience.
“We heard clearly from users that great AI should not only be smart, but also enjoyable to talk to. GPT‑5.1 improves meaningfully on both intelligence and communication style.”
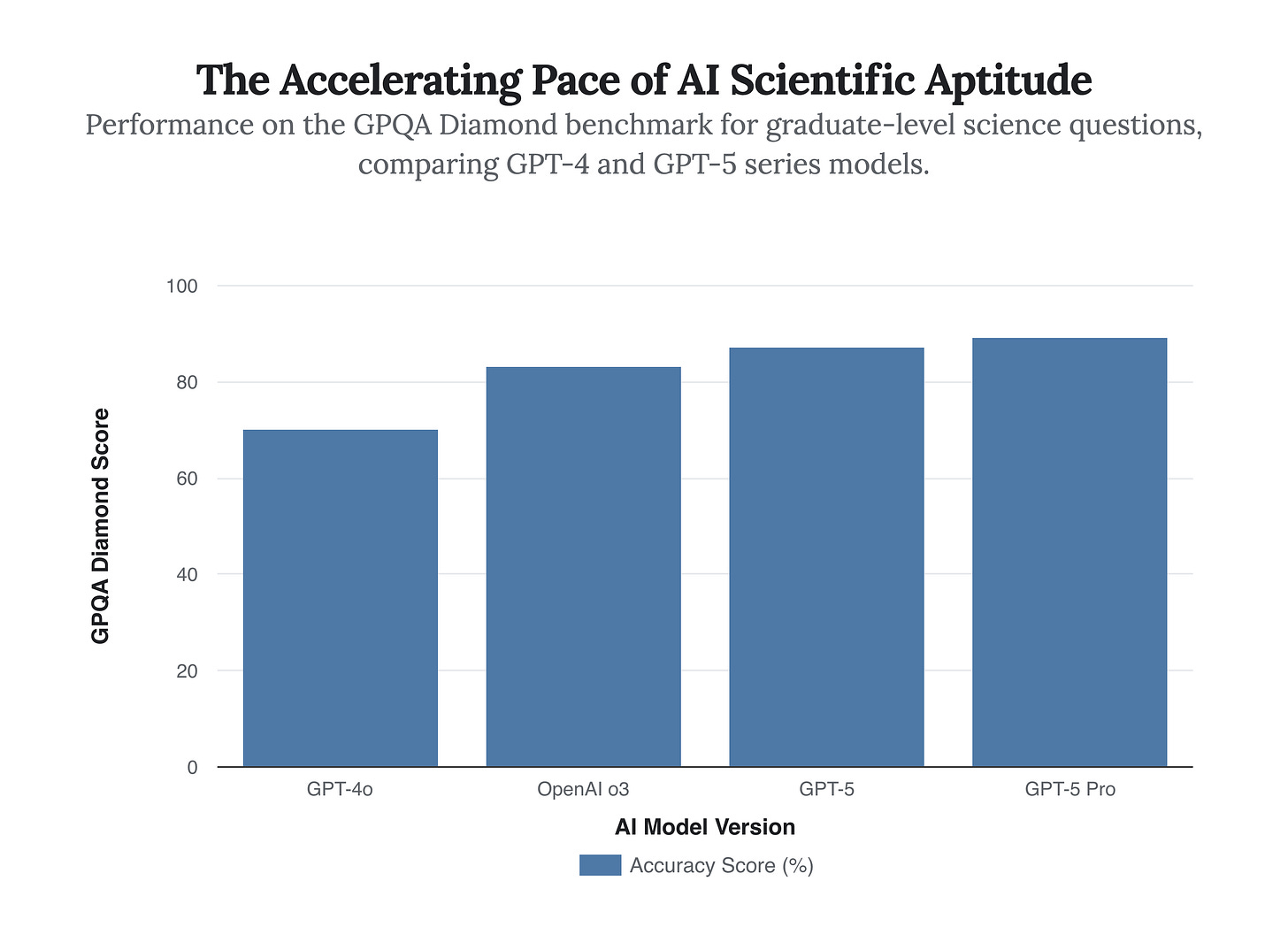
This new architecture is the latest step in a clear and rapid progression of AI capability. The performance of the underlying GPT-5 series on graduate-level scientific questions already demonstrated a significant jump from the GPT-4 era, showcasing a deep-seated improvement in the models’ understanding of complex subjects.
Beyond raw performance, the most profound changes in ChatGPT 5.1 are aimed at personalization and user experience. Following a rocky debut for GPT-5, which many users found to be robotic and less engaging than its predecessor, OpenAI has made a concerted effort to make 5.1 feel “warmer” and more conversational. The model now features eight distinct personality presets—including new additions like ‘Professional,’ ‘Candid,’ and ‘Quirky’—allowing users to tailor the AI’s tone to their specific needs.
In a blog post, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman highlighted the update’s focus on a more natural and personalized interaction, moving away from a one-size-fits-all approach.
Furthering this customization, ChatGPT 5.1 introduces a “Core Identity” profile, an optional feature that allows the AI to maintain a long-term, encrypted memory of user preferences, communication style, and ongoing projects. This allows for a level of personalization that begins to feel less like a tool and more like a true assistant that understands context and history across conversations. These changes, which apply instantly to all chats, mark a significant move toward an AI that adapts to the user, rather than the other way around.
Ultimately, the release of ChatGPT 5.1 is a landmark moment. It pushes the technical frontier with its superior reasoning capabilities while simultaneously addressing the fundamentally human desire for more natural and personalized interaction. It suggests that the future of AI is not just about raw intelligence, but about its ability to adapt its personality and reasoning to the specific user and task at hand.